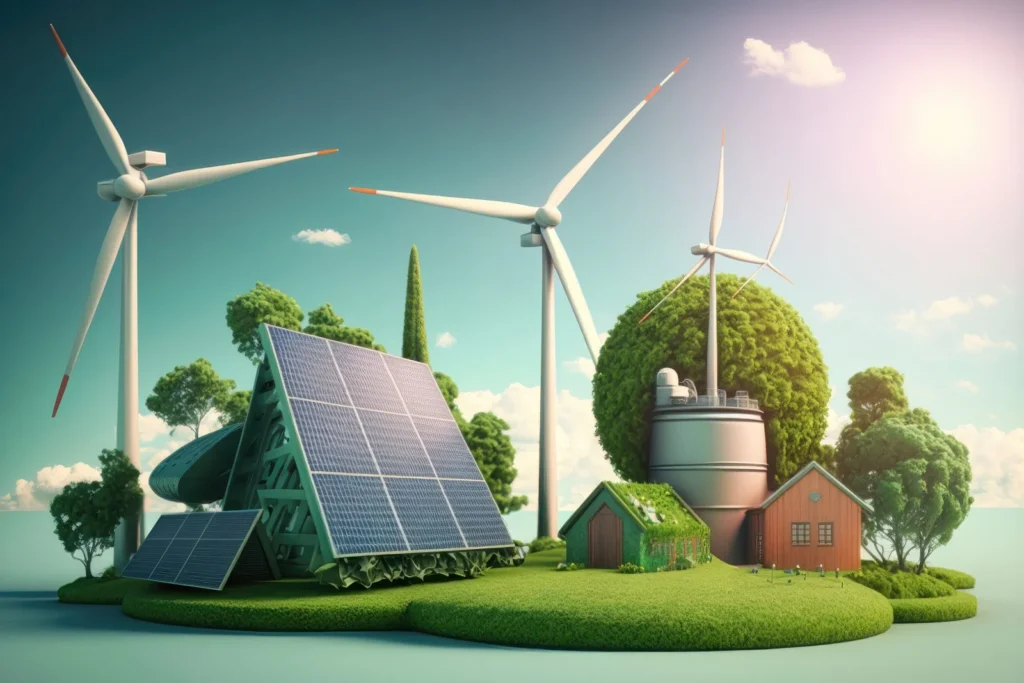
In an era defined by the urgent need to combat climate change, renewable energy has emerged as a critical solution. Among the most promising forms of renewable energy are solar, wind, and geothermal energy. These sources harness natural processes to generate power in ways that are both sustainable and environmentally friendly. Understanding the science behind these energy sources is key to appreciating their potential to transform our energy systems.
Solar Energy: Capturing Sunlight
How It Works
Solar energy is derived from the sun’s rays, which are an abundant and inexhaustible resource. Photovoltaic (PV) cells, commonly used in solar panels, are the cornerstone of solar energy technology. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect.
The photovoltaic effect occurs when photons from sunlight knock electrons loose from atoms in the semiconductor material. This movement of electrons generates an electric current, which is then captured and used as electricity. Solar panels often include an inverter to convert the direct current (DC) produced by the panels into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with most electrical grids.
Efficiency and Advances
The efficiency of solar panels has steadily improved over the years, thanks to advancements in materials and technology. Innovations like multi-junction solar cells and bifacial panels have increased the amount of electricity generated from the same amount of sunlight. Moreover, solar energy systems can now be paired with battery storage solutions, allowing for energy use even when the sun isn’t shining.
Wind Energy: Harnessing Air Currents
How It Works
Wind energy is generated by converting the kinetic energy of moving air into electricity. This process begins with wind turbines, which have large blades designed to capture the wind’s energy. As the wind blows, it causes the blades to spin. The spinning motion turns a rotor connected to a generator, which produces electricity.
The underlying science relies on aerodynamic principles. The blades of a wind turbine are carefully shaped to create lift, similar to an airplane wing. This lift causes the blades to spin efficiently, even at relatively low wind speeds. Modern wind turbines can adjust the pitch of their blades to optimize performance under varying wind conditions.
Site Selection and Scalability
The effectiveness of wind energy depends significantly on location. Ideal sites have consistent, strong winds and are often found in coastal areas, open plains, or offshore. Offshore wind farms, in particular, have become a major focus due to the stronger and more reliable winds found at sea.
Technological advancements have led to the development of larger turbines, capable of generating more power. For example, some offshore wind turbines now exceed 15 megawatts in capacity, enough to supply thousands of homes with electricity.
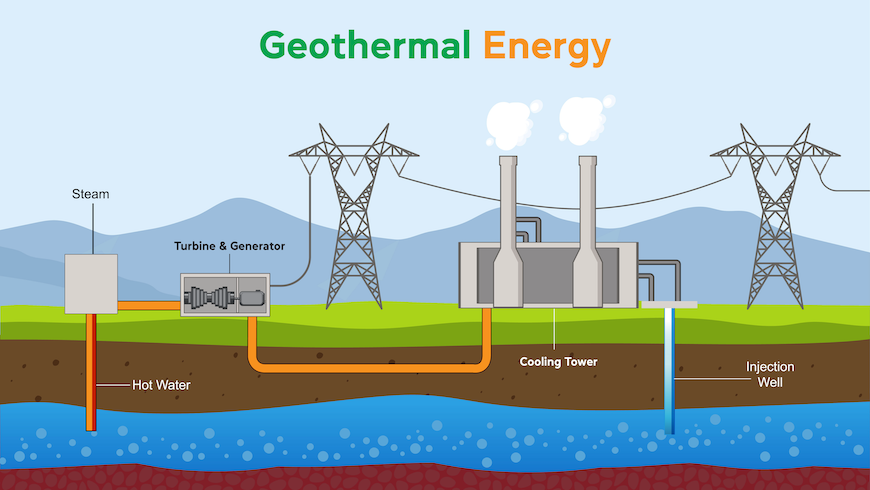
Geothermal Energy: Tapping Into Earth’s Heat
How It Works
Geothermal energy harnesses heat from beneath the Earth’s surface to generate electricity and provide heating. The Earth’s core is extremely hot due to the decay of radioactive elements and residual heat from the planet’s formation. This heat is conducted outward, warming rocks and water underground.
Geothermal power plants exploit this heat by drilling wells into geothermal reservoirs. Hot water or steam from these reservoirs is brought to the surface and used to drive turbines connected to generators. After the steam cools and condenses, it is often reinjected into the ground to sustain the resource.
Direct Use and Heat Pumps
Beyond electricity generation, geothermal energy can also be used directly for heating buildings, greenhouses, and even swimming pools. Geothermal heat pumps are another application, leveraging the stable temperatures found a few meters below the Earth’s surface to provide efficient heating and cooling for buildings.
Sustainability and Limitations
Geothermal energy is considered highly sustainable, as the heat extracted from the Earth is replenished naturally. However, its availability is geographically limited, as it requires specific geological conditions, such as volcanic activity or natural hot springs.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Reduced Carbon Emissions
One of the most significant advantages of solar, wind, and geothermal energy is their minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which release large amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants, these renewable sources provide clean energy with a much smaller environmental footprint.
Energy Independence
By utilizing locally available renewable resources, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and independence.
Economic Opportunities
The renewable energy sector has become a major source of job creation, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and research. Investments in renewable energy infrastructure also stimulate local economies and drive innovation.
Challenges and Future Directions
Intermittency and Storage
Solar and wind energy are intermittent by nature, as they depend on weather conditions. However, advances in energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage, are helping to mitigate these challenges.
Grid Integration
Integrating renewable energy into existing power grids requires upgrades to infrastructure and improved grid management. Smart grids, which use digital technology to monitor and manage energy flow, are playing a crucial role in this transition.
Geographical Constraints
While solar and wind energy can be deployed almost anywhere, geothermal energy is limited to regions with suitable geological conditions. Research into enhanced geothermal systems (EGS), which create artificial reservoirs, holds promise for expanding geothermal’s reach.
Conclusion
The science behind solar, wind, and geothermal energy showcases the incredible potential of renewable resources to power a sustainable future. As technology continues to advance, these energy sources are becoming more efficient, accessible, and cost-effective. By embracing renewable energy, we can reduce our environmental impact, enhance energy security, and create a more resilient energy system. The transition to renewable energy is not just a technological shift but a critical step toward addressing the global challenges of climate change and resource depletion.










